Flat roof insulation: types and pros & cons
There are three ways to insulate a flat roof. The difference has to do with the structure and method of insulating. In this article, you can read more on these differences and on the different types of roofing materials for flat roofs.
Types of flat roofs
The different types of flat roofs are: cold flat roof, warm flat roof and the inverted flat roof. They all have their own specific advantages and disadvantages. Which insulation method you should choose, depends on the existing construction and the available space.
| Method flat roof insulation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Warm flat roof | ||
| Cold flat roof | ||
| Inverted flat roof |
1. Warm flat roof
We speak of a warm flat roof when the insulation material is applied on top of the roof construction. The greatest advantage of this system is the protective function of the insulating material. The roof is slowly heated, along with the space beneath. As a result, the roof is less prone to big temperature changes.
The shrinkage- and expansion tension in both the roof construction and the roof seal will be lower as well. Another advantage of a warm flat roof is the fact that it, depending on the type of insulation material, remains walkable (more or less). The warm flat roof is applied most frequently.
Construction of the insulation in case of a warm flat roof
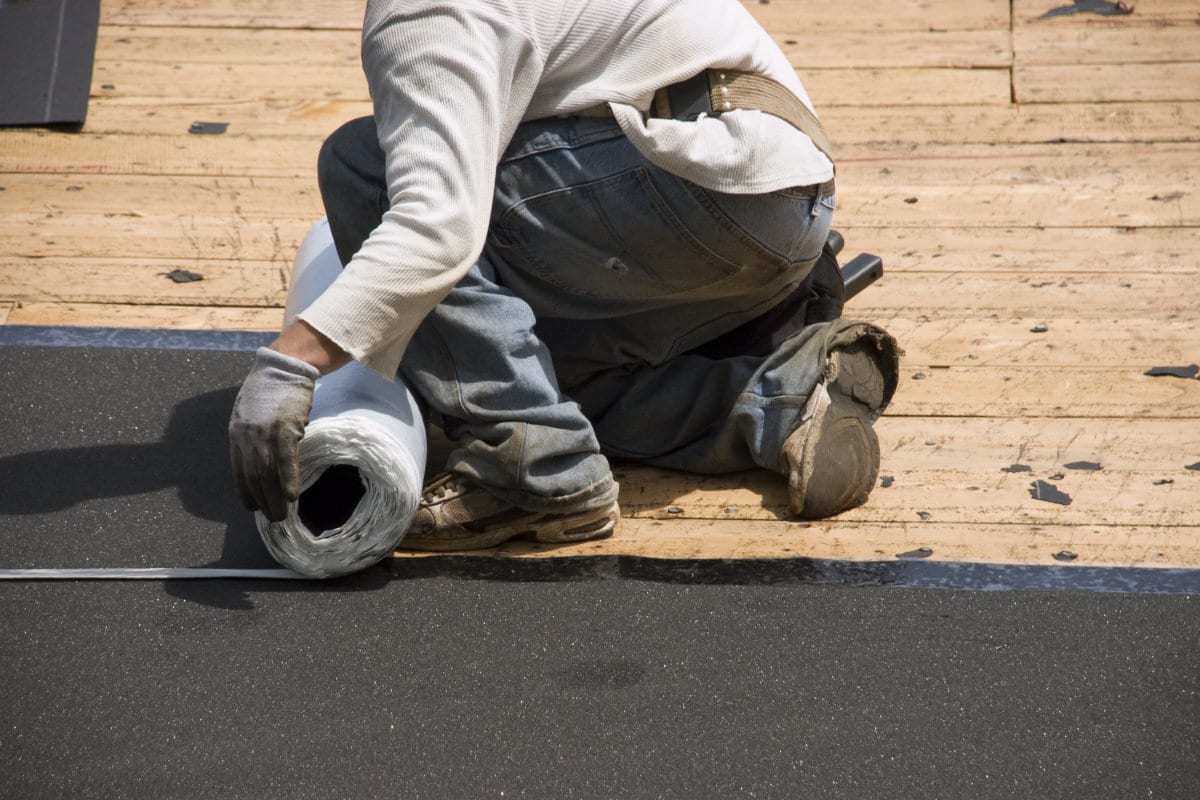
First of all, a damp-proof layer is applied onto the roof construction in order to prevent damp air from condensing in the insulation material. On top of this membrane, flat roof insulation boards that are barely sensitive to shrinkage or expansion are put into place. Think for example of rigid boards of sytrofoam, EPS, PIR or perlite.
The insulation boards must, as much as possible, be installed with a fall in order to guarantee a good drainage of rainwater. Eventually, the roofing – which functions as a water-repellent layer – will be installed on top of the flat roof insulation boards. The roof covering can be finished with tiles or gravel. Depending on the thickness of the insulation material, it may be required to raise the roof edge. This should prevent rainwater from streaming over the roof in case of heavy showers.
Advantages warm roof insulation
- Offers good protection to the roof
- Insulates very well
- Corners are easier to insulate
Disadvantages warm roof insulation
- Labour-intensive
- Only executable in good weather conditions
- Risk of damage to the roof covering
Guide price warm flat roof: £65 – £105 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for a warm flat roof.
2. Cold flat roof
We speak of a cold flat roof when the insulation material is applied to the bottom side of the roof boarding. The roof is not heated by the space below and it is prone to weather conditions such as temperature changes caused by heat or frost. Consequently, the roof construction and the sealing layer will shrimp or expand as a result of which damage can occur over time.
For this reason, a cold flat roof should be avoided as much as possible. However, sometimes a warm flat roof construction is not an option due to technical restrictions. In cases like that, one can opt for insulation according to the cold roof principle as this is still better than no insulation at all.
Construction of the insulation in case of a cold flat roof
When insulating a flat roof, one mostly uses glass- or rock wool. This material is applied between the beams of the roof boarding. If the ceiling is made of concrete, professionals usually build a wooden construction (suspended ceiling) in which the insulation material can be applied. As for systems like this, it is important to provide a good damp barrier. Otherwise, condensation problems might occur.
Insulate cold flat roof: advantages
- When a warm roof construction is not possible, it is still better to use this method instead of not insulating a flat roof at all.
Insulate cold flat roof: disadvantages
- In case of a cold roof, there is always a risk of condensation. The construction itself is not protected against weather influences either.
Guide price cold flat roof: £25 – £35 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for a cold flat roof.
3. Inverted flat roof
If renovation activities are carried out but the current roofing should stay in place, an inverted flat roof is usually applied. The insulation material is installed on top of the existing roof sealing. The roofing eventually serves as a water barrier. The thermal insulation value of this insulation method is not as good as compared to a warm roof. On the other hand, the costs of an inverted roof will be lower.
Construction of insulation inverted flat roof
The existing roofing functions as a waterproof layer. Damp-proof XPS boards (extruded polystyrene) are installed on top of the roofing. Roofers cover the boards with ballast like gravel or tiles in order to make sure that the insulation material remains in place.
Advantages inverted flat roof
- Easily executable, interesting in case of renovation.
- No extra vapour barrier required.
- Generally cheaper than a warm roof.
Disadvantages inverted flat roof
- The ballast layer involves extra weight. The roof construction must be able to withstand this.
- The corners are harder to insulate.
- The insulating effect is not as good as compared to warm roof constructions.
Guide price inverted flat roof: £40 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for an inverted flat roof.

Flat roof insulation: prices
If you are planning to insulate a flat roof, it always pays off to compare prices of different roofers. Thanks to the quote service of roof-info.co.uk, you can directly request price quotes from different professionals, without any further obligation. Click here for more information.
Types of roof covering
There are a few types of roof covering materials. Bitumen is most widely used, as well as synthetic materials like EPDM and polyester.
| Type of roofing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bitumen | ||
| EPDM | ||
| PVC | ||
| Green roof |
 1. Bitumen roofing
1. Bitumen roofing
Bituminous sealings (on the base of petroleum) have evolved significantly over the years. Nowadays, bitumen is primarily used on the base of polymer. This material is provided with polyester or fibreglass, as a result of which it is very strong and resistant to cracks.
There are two types of polymer-based bitumen: APP and SBS. APP is resistant to UV and high temperatures. Moreover, it does not need a protective layer of ballast. SBS is slightly more flexible and it sticks better than APP. However, SBS is more sensitive to bright sunlight. For this reason, this material has a protective layer (slate). This way, it can be applied without a ballast layer.
Guide price flat roof bitumen: £35 – £45 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for a flat roof with bitumen.
 2. Synthetic roofing: EPDM
2. Synthetic roofing: EPDM
EPDM is synthetic rubber. For applications on the roof, one completely customises the material and applies it to the roof in one piece. This way, the risk of leaks is reduced as much as possible. The foil is usually attached by means of glue, although hot air is used sometimes.
In the latter case, a special EPDM membrane is used: the edges are provided with an elastomer that becomes fluid when it is heated, as a result of which the seams can be sealed well. The seams and the connection to the edges are the biggest concern when using EPDM. This material is very sustainable. Sometimes, there is even a guarantee of 30 years.
Guide price flat roof with EPDM: £45 – £70 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for a flat roof with EPDM.
 3. Synthetic roofing: PVC
3. Synthetic roofing: PVC
This plastic foil (which is available in rolls) is applied onto the roof structure in overlapping strips. This is done by means of glue, possibly in combination with hot air. If a special foil is used, PVC can actually be glued onto an existing layer of bitumen.
This foil is provided with a protective layer. In case of a green roof, an armament of fibreglass is often used in order to protect the membrane against roots. PVC is slightly more sensitive to UV than EPDM, but the connections of the seams are significantly better. On average, PVC will last about 20 to 25 years.
Guide price flat roof with PVC: £40 – £70 per m²
⇒ Request free quotes for a flat roof with PVC.
 1. Bitumen roofing
1. Bitumen roofing 2. Synthetic roofing: EPDM
2. Synthetic roofing: EPDM 3. Synthetic roofing: PVC
3. Synthetic roofing: PVC